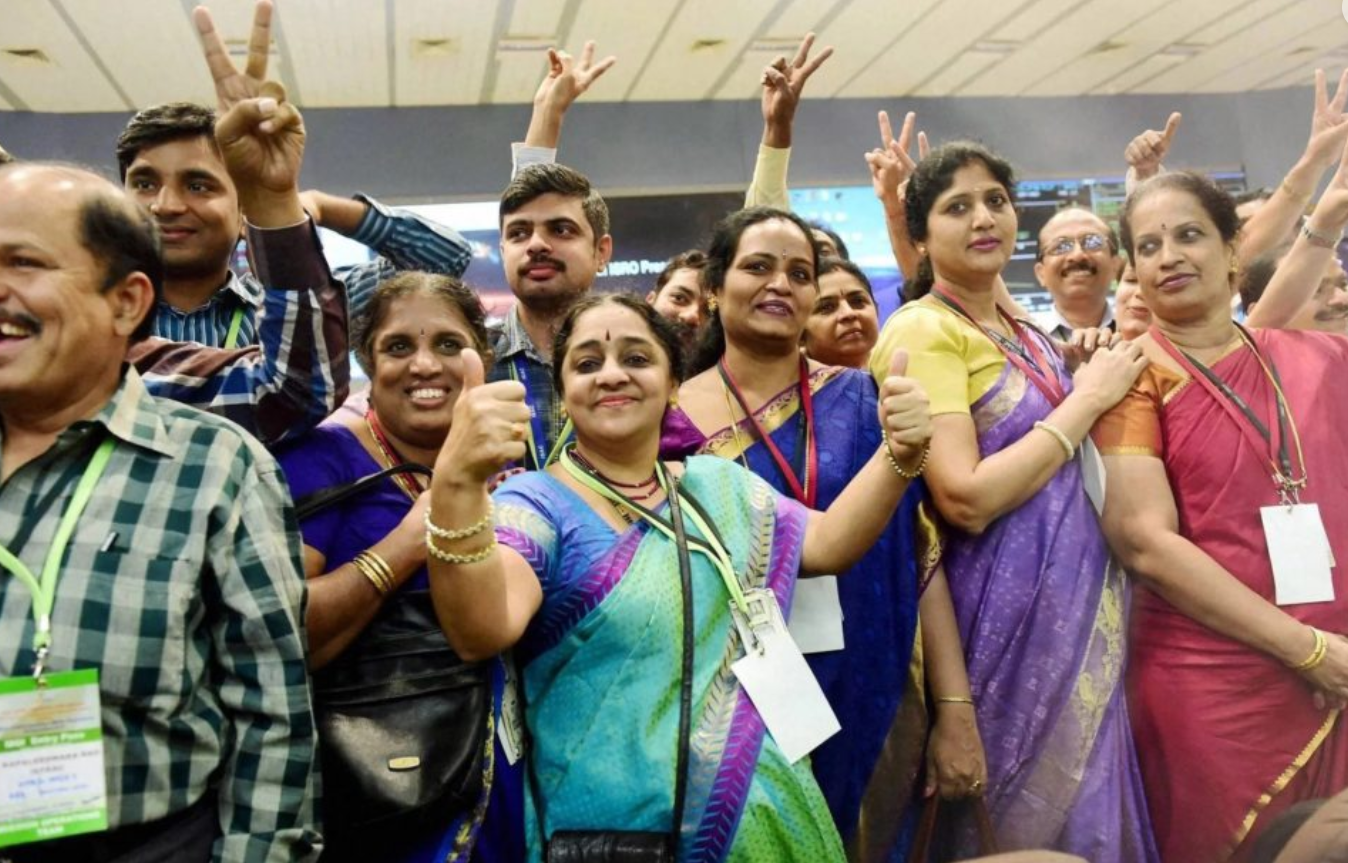
LVM3-M4 / Chandrayaan-3 Mission
soft-land on the Moon’s surface on August 23rd

"ISRO's GSLV Mk III, known as 'Bahubali', is India's heaviest and most powerful rocket, designed for launching heavy payloads into space."
Chandrayaan-1 was the first lunar space probe of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) which operated in 2008–09. It found water on the Moon and confirmed the discovery of water locked in minerals on the Moon using NASA’s Moon Minerology Mapper (M 3), an imaging spectrometer.
Chandrayaan-2 was launched in July 2019 and was India’s second lunar exploration mission after Chandrayaan-1. It consisted of an orbiter, a lander named Vikram, and a rover named Pragyan. The mission aimed to study the south polar region of the Moon and gather information about its topography, mineralogy, and exosphere.
Chandrayaan-3 is a follow-up mission to Chandrayaan-2 that will attempt to land a spacecraft on the moon and collect data on the composition and geology of the moon. It will also conduct scientific experiments to study the moon’s environment, including its history, geology, and potential for resources.the launch of Chandrayaan-3 took place on July 14 at 2.35 p.m. (IST) , with soft-land on the Moon’s surface on August 23rd, 2023 .


August 18, 2023
A delegation from the Sultanate of Oman, headed by H.E. Eng. Said Hamood Said Al Maawali, Honourable Minister of Transport, Communication, and Information Technology (MTCIT), visited ISRO Headquarters for a meeting with Chairman, ISRO/Secretary, DOS, Mr. Somanath.S., on August 17, 2023, to discuss India-Oman space cooperation. The Minister was accompanied by senior officials from the Sultanate of Oman, including Dr Saoud Humaid Salim Al Shoaili, Head-National Space Program.
Senior ISRO officials, including Mr Shantanu Bhatawdekar, Scientific Secretary, ISRO, and Dr. Prakash Chauhan, Director of ISRO's National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC), also participated in the meeting.

August 17, 2023
A high-level delegation from Mauritius, led by the Honourable Minister for Information Technology, Communication and Innovation (MITCI), Mr. DarsanandBalgobin, paid a fruitful visit to ISRO on August 17, 2023. Honourable Minister was accompanied by the Chairman of the Board of the Mauritius Research & Innovation Council, Dr.Kaviraj Sharma Sukon. The delegation had a meeting withShri Somanath S, Chairman, ISRO/Secretary, DOS at the ISRO Telemetry, Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC) in Bengaluru.Director of U R Rao Satellite Centre Mr. M Sankaran; Scientific Secretary of ISRO Mr. Shantanu Bhatawdekar; Director of National Remote Sensing Centre, Dr. Prakash Chauhan and other senior officials were also part of the discussion.
Chairman, ISRO/ Secretary, DOSwhile thanking Mauritius for hosting ISRO’s station for about 3 decades, outlined potential applications of space technology that could benefit Mauritius.The Honourable Minister highlighted the specific requirements and aspirations of Mauritius.

August 14, 2023
Indian Space Research Organisation, ISRO is organising a Workshop on Space Situational Awareness & Space Traffic Management (SSA & STM) meant for Indian students, researchers, and faculty members during October 12-14, 2023 at the ISRO Headquarters in Bengaluru.
SSA is the comprehensive knowledge of the Space environment, including the location, orbit, and function of all man-made objects in Space, as well as natural objects / phenomena such as Space weather, asteroids and comets. It is essential for preventing collisions between objects in Space and mitigating the effects of Space debris to support safe, stable and sustainable outer Space activities. STM is the process of ensuring the safe and efficient operation of all Space objects. STM includes the collection and analysis of SSA data, the development of collision avoidance procedures, and the implementation of those procedures. STM is also responsible for the safe disposal of Space debris.

August 11, 2023
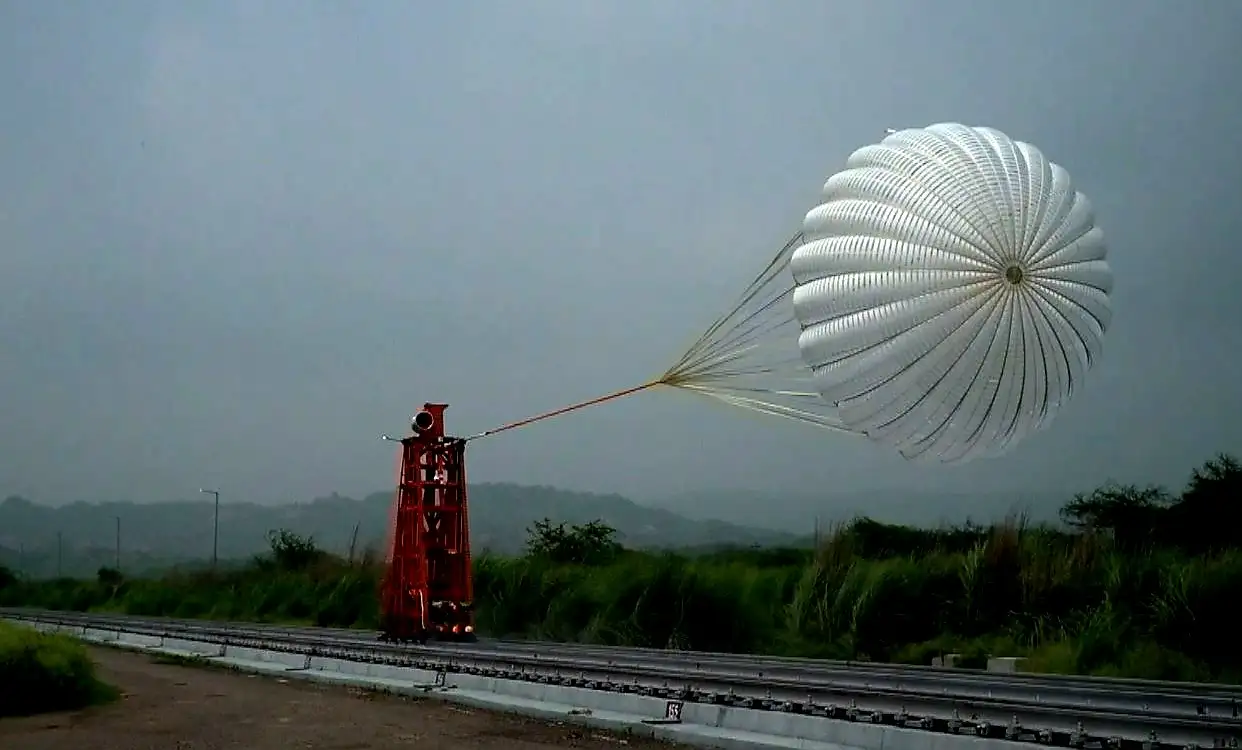
Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC)/ISRO, successfully conducted a series of Drogue Parachute Deployment Tests at the Rail Track Rocket Sled (RTRS) facility of the Terminal Ballistics Research Laboratory, Chandigarh, during August 8-10, 2023. The tests were conducted in collaboration with Aerial Delivery Research and Development Establishment (ADRDE)/DRDO.
The Gaganyaan mission entails the safe transportation of astronauts to space and back. A crucial component of this mission is the deployment of drogue parachutes, which play a pivotal role in stabilizing the crew module and reducing its velocity to a safe level during re-entry.
Drogue parachutes, packed within pyro-based devices known as mortars, are ingeniously designed to eject the parachutes into the air upon command. These conical ribbon-type parachutes, boasting a diameter of 5.8 meters, employ a single-stage reefing mechanism, ingeniously minimizing canopy area and mitigating opening shock, ensuring a smooth and controlled descent.

August 8, 2023
Exploration of space beyond the near-Earth regime has been one of the most challenging and fascinating ventures of humankind and continues to capture the imagination of generations. Over the ages, several space-faring nations have undertaken numerous missions to explore most of the planets in the solar system, their natural moons, various minor planets/ asteroids, comets and even interplanetary voyages. The Moon and Mars are the most explored and also comparatively more crowded planetary bodies at present. India’s Chandryaan-3 (CH3) is the latest entry into the lunar orbit. More intensified activities around the Moon are foreseen in the next few years due to the renewed interest in lunar exploration, heralded by Artemis missions for return to the Moon and preparations for colonisation of Mars. While the previous missions were essentially aimed at scientific explorations, upcoming ventures will likely involve multiple actors of diverse interests, including those primarily driven by resource utilisation for commercial purposes. A better understanding of theenvironment is needed to formulate reasonable mitigation practices to avoid close-approach threats in planetary orbits.
The current Space Debris Mitigation Guidelines by the UN and Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee (IADC) are applicable to spacecraft and orbital stages “that will be injected into Earth orbit.Currently space debris pose a major threat to the long-term sustainability of outer space activities in the ever-increasingly congested Earth orbits. Therefore, based on the lessons learnt while operating in the near-Earth regime, it is interesting and desirable to undertake studies related to close approaches in view of the increasing number of objects in the lunar orbits.
July 22, 2023
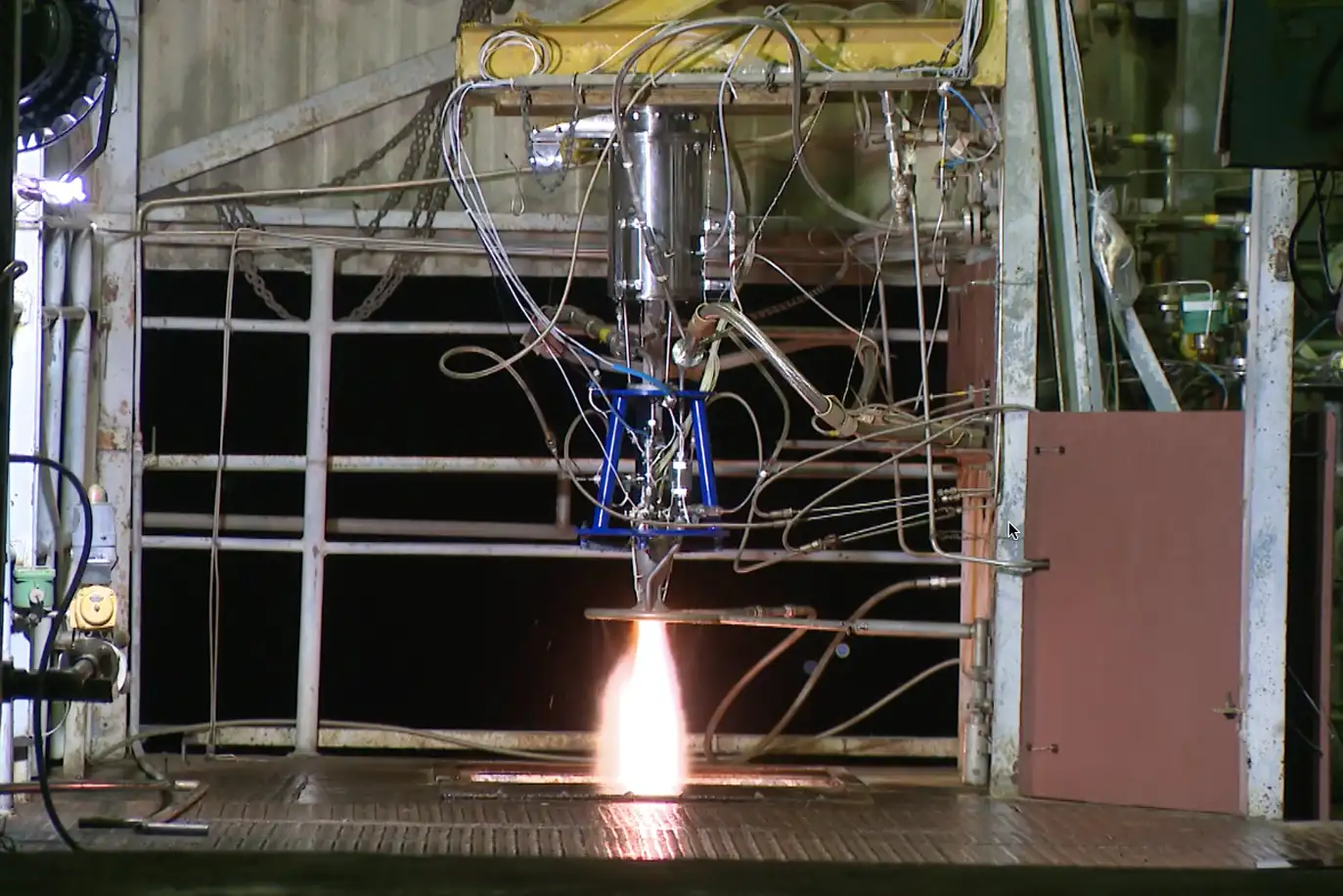
On July 21, 2023, ISRO demonstrated its commitment to fostering the space ecosystem in India by enabling a successful rocket-engine test conducted by Skyroot, a Hyderabad-based space start-up, at ISRO Propulsion Complex (IPRC) Mahendragiri. The test took place in the Liquid Thruster Test Facility (LTTF) in IPRC. The testing was enabled by IN-SPACe.
The test involved the Raman-II engine, which was designed by Skyroot to generate 820 N (Sea Level) and 1460 N (Vacuum) thrust, with a nominal chamber pressure of 8.5 bar absolute. The regeneratively cooled engine, manufactured through additive manufacturing techniques, utilizes Mono Methyl Hydrazine and Nitrogen Tetroxide as propellants. The 10-second duration test achieved the expected performance in terms of start transient, steady state, and shut-off. Skyroot intends to integrate the Raman-II engine into the fourth stage of its launch vehicle, Vikram-I.
August 17, 2023
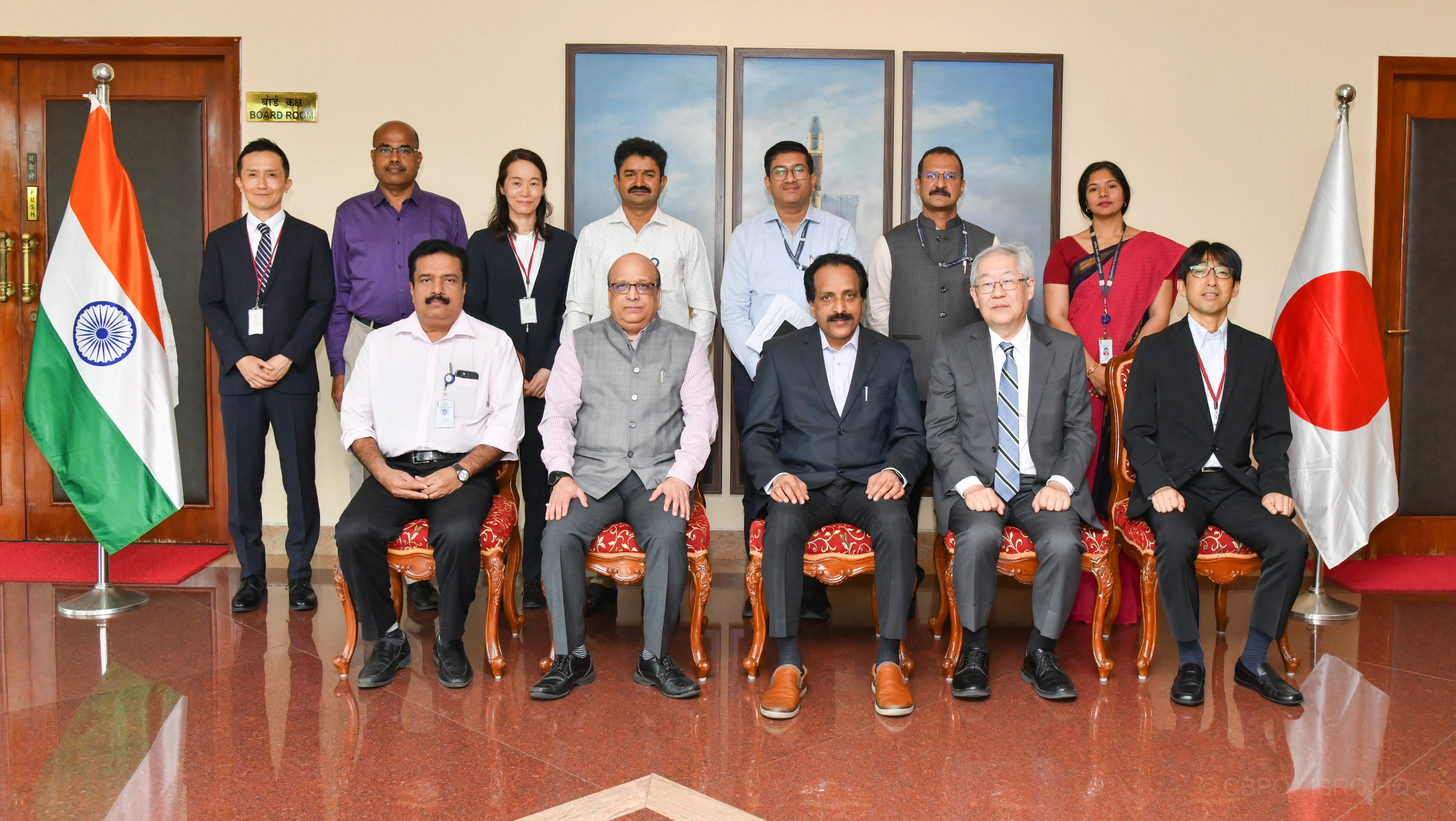
Dr. Saku Tsuneta, Vice-Chair of Japan’s Cabinet Committee on National Space Policy (CNSP) and Director General, National Astronomical Observatory of Japan (NAOJ) visited ISRO Headquarters on August 08, 2023 and had a meeting with Shri S. Somanath, Chairman, Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) / Secretary, Department of Space (DOS). India-Japan space science cooperation at national level, Space Agency level (ISRO & JAXA) and institutes-level were discussed with specific reference to the proposed Joint LUPEX (Lunar Polar Exploration) Mission. Potential cooperation opportunities in: i) Utilisation of data from Adithya L1 and Chandrayaan-3 missions; ii) Development of smaller lander for lunar exploration; and iii) Joint activities under QUAD Space working group were also discussed.









